눈
눈의 해부학적 구조와 눈의 움직임을 조절하는 근육에 대한 암기를 바탕으로, 특정 뇌신경에 문제가 생겼을 때 눈의 어떤 움직임에 문제가 생기는지 유추할 수 있어야 한다. 기능적 차원에서 시각 전도로에 대한 문제도 자주 출제되며, 방수의 흐름에 대한 내용도 알고 있는 것이 좋겠다.
1. 해부학
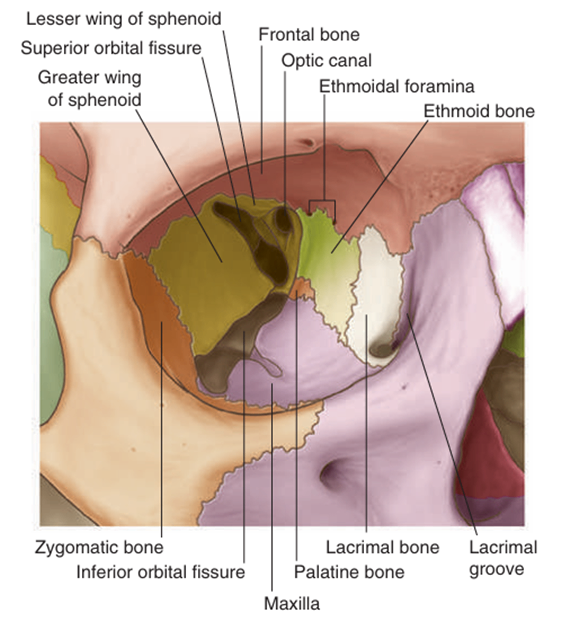
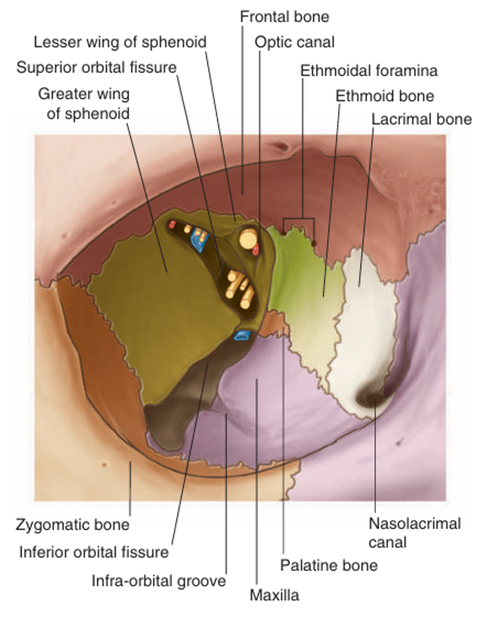
1) 눈확뼈(bony orbit)
Gray’s anatomy for students 4th ed. pp.916 | (1) 눈확뼈의 구조 ① Frontal bone (위쪽 뒷벽) ② Zygomatic bone (가쪽벽) ③ Maxilla (앞쪽 아래벽) ④ Sphenoid bone (뒷벽) ⑤ Ethmoid bone (안쪽벽) ⑥ Lacrimal bone (안쪽벽) ⑦ Palatine bone (아래벽) |
| Gray’s anatomy for students 4th ed. pp.923 | |
틈새/구멍 | 통과 구조 | |
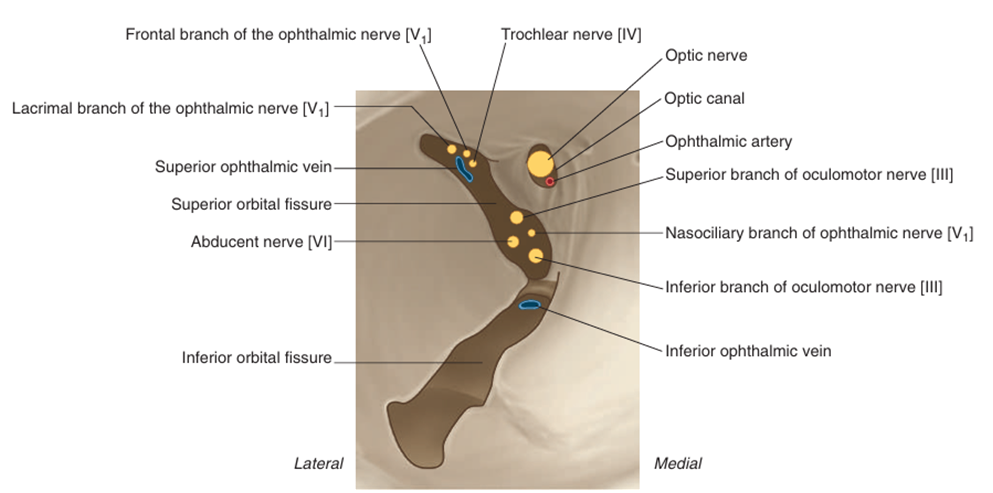
Optic canal | optic n.(CN II), ophthalmic a. | |
Superior orbital fissure | oculomotor n.(CN III)의 위, 아래가지, trochlear n.(CN IV), abducent n.(CN VI), ophthalmic n.(CN V1)의 lacrimal branch/frontal branch/nasociliary branch, superior ophthalmic v. | |
Inferior orbital fissure | maxillary n.(CN V2), maxillary n.의 zygomatic branch, inferior ophthalmic v. | |
Infra-orbital foramen | infra-orbital n., a., v. | |
Anterior/posterior ethmoidal foramen | anterior/posterior ethmoidal n., a., v. | |
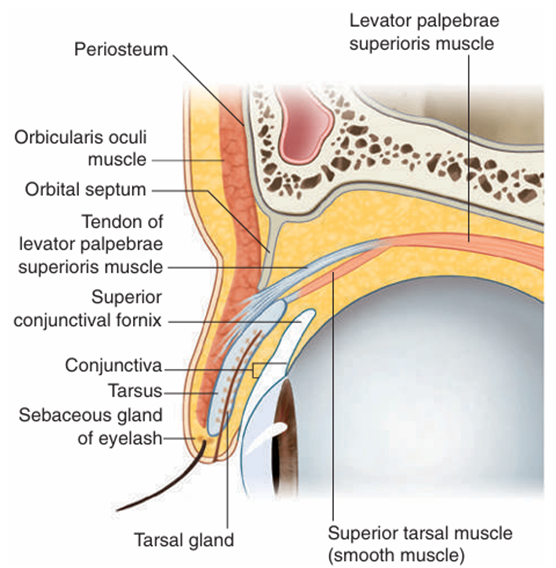
2) 눈꺼풀
Gray’s anatomy for students 4th ed. pp.917 | ① Orbicularis oculi m.(눈둘레근)의 눈꺼풀부분: 수축 시 눈을 감음 • Facial n. (CN VII) 분포 • 손상 시 눈 못 감고, 아랫눈꺼풀 처짐 ② Levator palpebrae superioris m.(눈꺼풀올림근): 수축 시 눈을 뜸 (위눈꺼풀을 올림) • Oculomotor n. (CN III) 분포 • 손상 시 눈꺼풀처짐(ptosis)
③ Superior tarsal m.(위눈꺼풀판근): 눈꺼풀올림근을 도움 • 교감신경 분포 • 손상 시 부분눈꺼풀처짐(partial ptosis) • 호너증후군의 눈꺼풀처짐 기전 |
3) 안구의 근육
(1) intraocular(intrinsic) muscle
① 동공 조절 근육: 눈으로 들어오는 빛의 양 조절
• 동공조임근(sphincter pupillae m.): 동공 수축
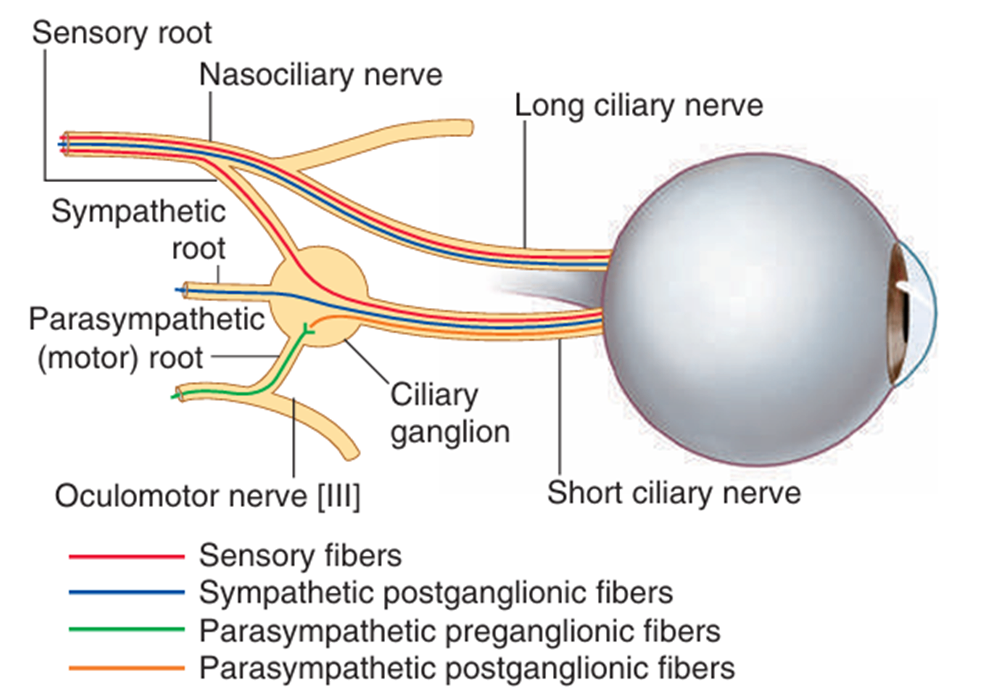
- short ciliary n. 중 CN III의 부교감 성분 분포
• 동공이완근(dilator pupillae m.): 동공 확장
- internal carotid plexus 기원 교감 성분 분포
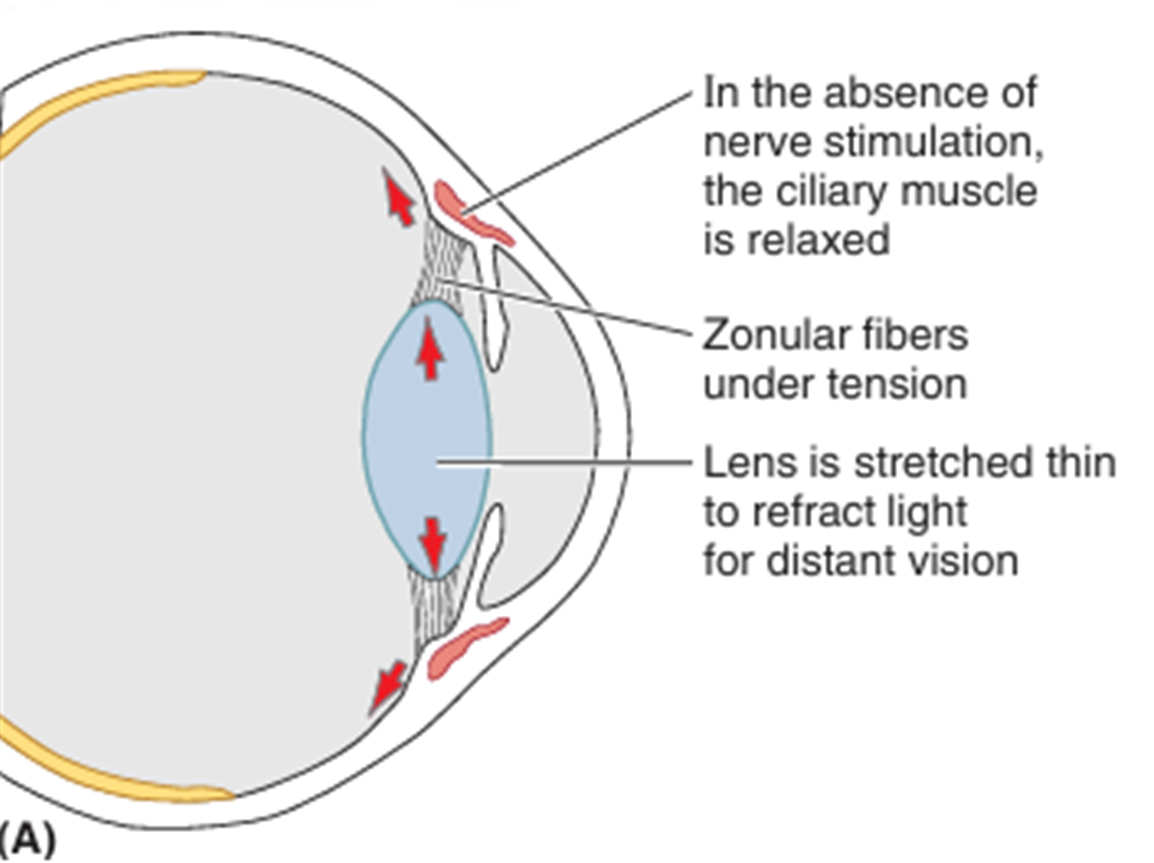
② 모양체근(ciliary m.): 수정체 두께 조절
• 가까운 것을 볼 때: 모양체근 수축 → 섬모체 수축 → zonular fiber 이완 → 렌즈 두꺼워짐
• CN III의 부교감 성분 분포
| |
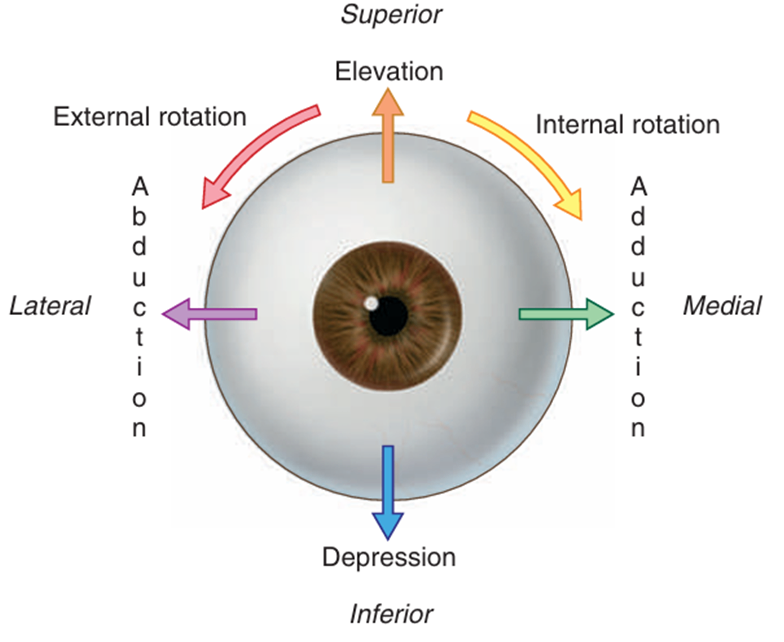
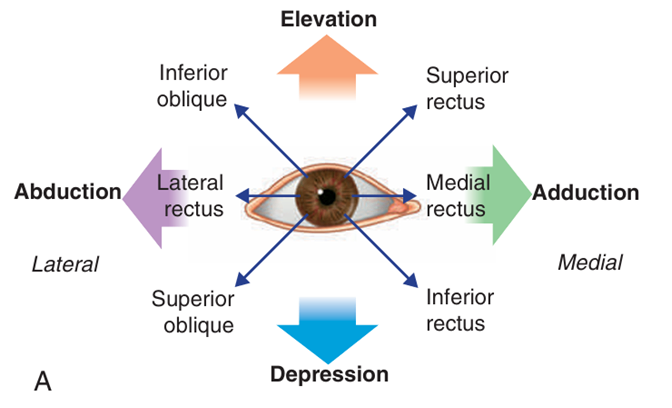
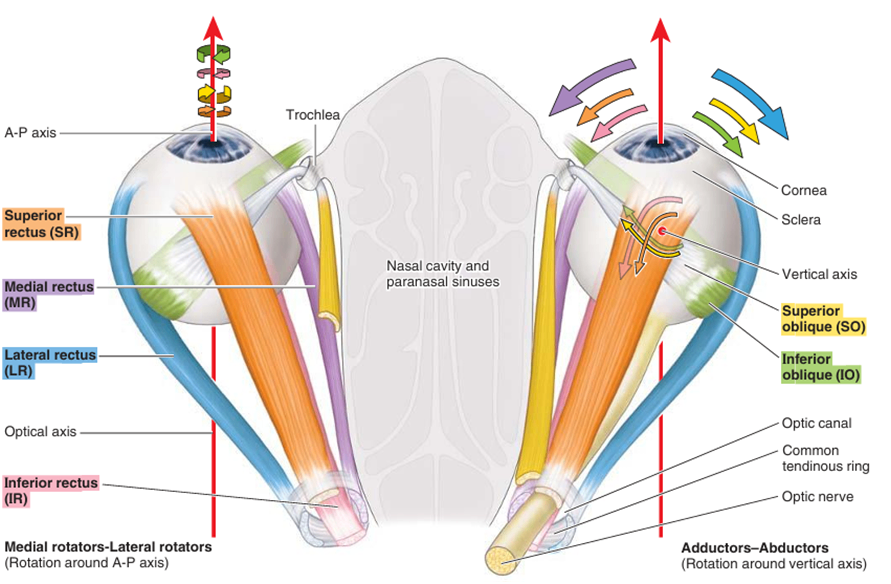
(2) 안구의 운동
Gray’s anatomy for students 4th ed. pp.926 | ① 올림(elevation), 내림(depression) : 가로축 기준 회전 ② 모음(adduction), 벌림(abduction) : 수직축 기준 회전 ③ 안쪽으로 돌림(internal rotation), 바깥쪽으로 돌림(external rotation) : 앞뒤축 기준 회전 |
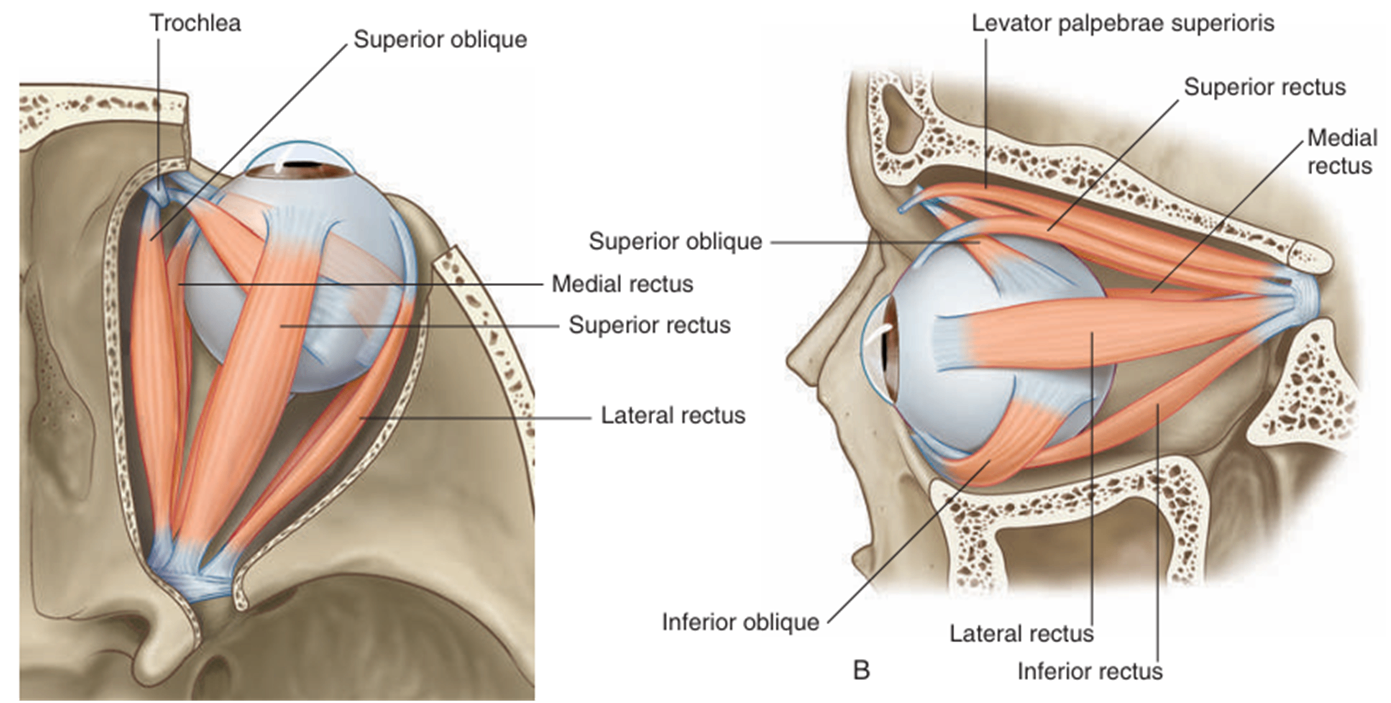
(3) extraocular(extrinsic) muscle
• 온힘줄고리(common tendinous ring, annulus of Zinn): 눈확뼈막(periorbita)이 두터워진 부위
| ||||
근육 | 이는곳 | 닿는곳 | 신경지배 | 안구 움직임 |
위곧은근 (superior rectus m.) | 온힘줄고리 (Annulus of Zinn) | 안구의 위쪽 앞 절반 | CN III - 위가지 | elevation adduction medial rotation |
아래곧은근 (inferior rectus m.) | 안구의 아래쪽 앞 절반 | CN III - 아래가지 | depression adduction lateral rotation | |
안쪽곧은근 (medial rectus m.) | 안구의 안쪽 앞 절반 | adduction | ||
가쪽곧은근 (lateral rectus m.) | 안구의 가쪽 앞 절반 | CN VI | abduction | |
위빗근 (superior oblique m.) | 시각신경관 위쪽 나비뼈 몸통 | 안쪽의 안구의 바깥 뒤 사분역(위면) | CN IV | depression, abduction, internal rotation |
아래빗근 (inferior oblique m.) | 위턱뼈의 눈확면,코눈물관의 가쪽 | 안구의 바깥 뒤 사분면(아래면) | CN III - 아래가지 | elevation abduction external rotation |
• 안구근육 신경 외우기: LR6SO4R3 (R: 나머지)
• 근육은 안구의 축이 아닌, 눈확의 축을 따라 안구에 부착되어 다양한 작용을 하게 됨
• 실제 안구의 움직임은 여러 근육의 협동작용에 의해 나타남
ex. pure elevation: IO + SR
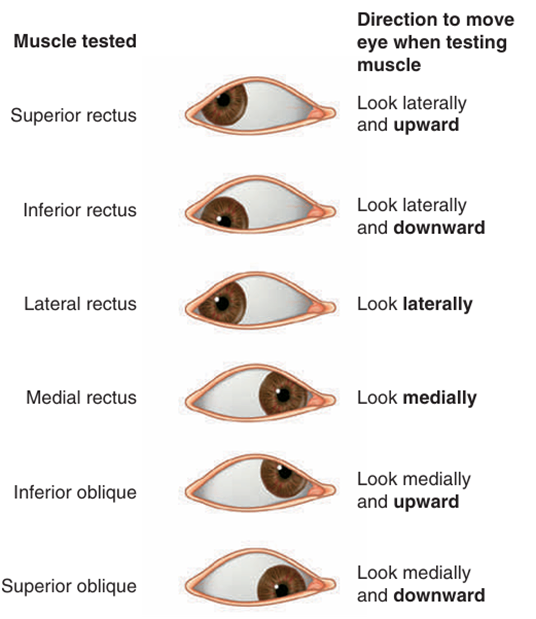
• 안구근육 검사: 눈을 가쪽이나 안쪽으로 움직여 안구의 축과 검사하고자 하는 근육의 장축을 일치시킨 후 검사
안구근육의 작용 | 안구근육 검사 |
| |
4) 혈관계
(1) 동맥: 눈동맥(ophthalmic a.)이 공급 ← 속목동맥(ICA)
• 중심망막동맥(central retinal a.): 손상 시 시각 손실
(2) 정맥: 위/아래눈정맥(superior/inferior ophthalmic v.)
• 해면정맥굴(cavernous sinus)와 연결: 머리 안으로 감염 파급 가능
5) 신경분포
(1) Oculomotor n. (CN III)
• intrinsic m.: sphincter pupillae m., ciliary m. (short ciliary n.의 부교감 성분)
• extrinsic m.: SR, MR, IR, IO, 눈꺼풀올림근
(2) Trochlear n. (CN IV)
• extrinsic m.: SO
(3) Abducens n. (CN VI)
• extrinsic m.: LR
(4) Facial n. (CN VII)
• orbicularis oculi m., frontalis m.
(5) 교감성분
• dilator pupillae m. (short, long ciliary n.의 교감성분), 위눈꺼풀올림판근
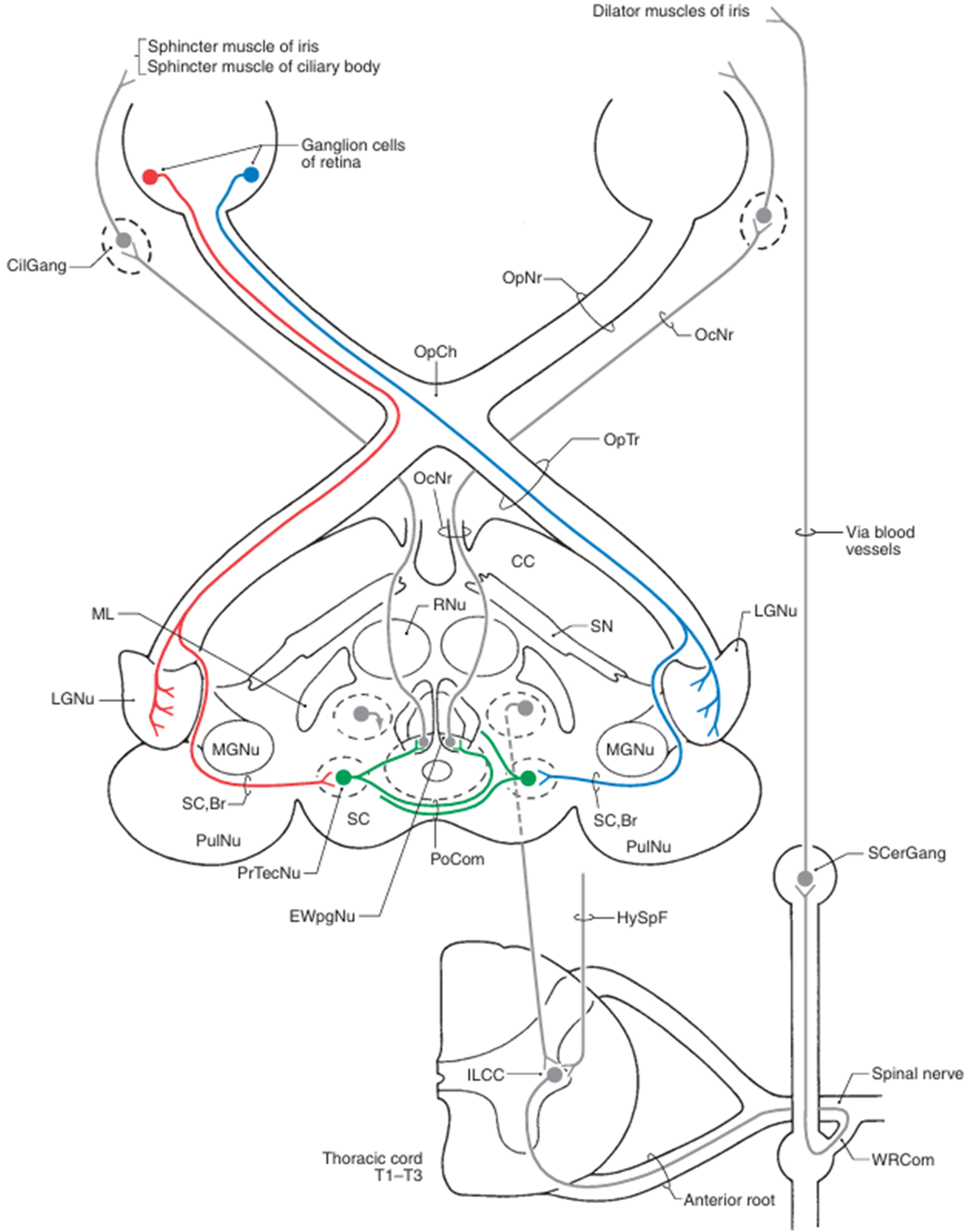
2. 시각 전도로
1) 시야(visual field)
(1) 기준: 나(실험자)
(2) 4분할: superior/inferior, nasal(medial)/temproal(lateral)
2) retinal field: 망막에 상이 맺힌 영역; 시야와 상하좌우 반전
(1) 중심: 중심오목(fovea)
3) 입체시(stereoscopic vision): 양 눈의 시야가 겹치는 binocular zone에 있는 물체에 대해서는 양 눈에서 온 시각 정보가 합쳐져 원근감 인식
(1) convergence: 일차시각영역의 layer II, III에서 합쳐짐
4) 시각전도로: Optic nerve → Optic chiasm → Optic tract → dLGN → Optic radiation → 일차시각영역
(1) Optic nerve: 망막에서 인식한 빛의 신호 전달
• 신호 전달 경로: photoreceptor cell(감각뉴런) → interneuron → retinal ganglion cell(RGC)
• RGC의 엑손이 optic disc로 나가 이어지는 경로를 구간에 따라 optic nerve/chiasm/tract로 구분
• 종류: medial(nasal)/lateral(temporal) retinal axon; 각각 눈과 같은/반대쪽 시야의 정보 전달
(2) 시신경교차(Optic chiasm): medial retinal axon의 교차가 이루어짐
• 결과: 왼쪽 시야는 오른쪽 optic tract으로, 오른쪽 시야는 왼쪽 optic tract으로 전달
• 시신경교차 전 왼쪽 optic n. 손상 시 왼쪽 눈이 안 보임
• 시신경교차 후 왼쪽 optic tract 손상 시 양쪽 눈의 오른쪽 시야가 안 보임
Visual Field | Optic Nerve | Optic Chiasm | Optic Tract |
Lt. Visual Field | Lt. eye medial retinal axon | 교차 O | Rt Optic Tract |
Rt. eye lateral retinal axon | 교차 X | ||
Rt. Visual Field | Lt. eye lateral retinal axon | 교차 X | Lt Optic Tract |
Rt. eye medial retinal axon | 교차 O |
(3) Optic tract: 뇌와 시냅스 형성
① dosal Lateral Geniculate Nucleus of thalamus (dLGN): visual perception
② Superior colliculus of the midbrain: eye movement
③ Pretectal area of the midbrain: pupillary light reflex
④ Suprachiasmatic nucleus(SCN) of Hypothalamus: circadian rhythm
⑤ 기타
(4) Optic radiation: dLGN → 일차시각영역(후두엽)
(5) topographic map: 입체시 형성 전까지 시야의 상하좌우가 반전된 상의 위치정보 그대로 보존
| 오른쪽 위 사분면의 시야 → retinal field의 왼쪽 아래에 상 맺힘 → 왼쪽 optic tract → 왼쪽 아래 dLGN → 왼쪽 아래 optic radiation → 왼쪽 아래 일차시각영역 |
5) 시각전도로의 손상
(1) -anopsia: 보이지 않는 상태
• hemianopsia: 시야의 절반이 보이지 않는 상태
• quadrantanopsia: 시야의 1/4이 보이지 않는 상태
(2) homonymous, heteronymous
• homonymous: 양쪽 눈의 동일한 영역의 시야 손상
• heteronymous: 양쪽 눈의 서로 다른 영역의 시야 손상
(3) 시각전도로의 손상
<시각전도로> Haines Atlas of Neuroanatomy 9th ed. pp.278 | <시각전도로의 손상> |
6) visual association cortex
(1) magnocellular system(dorsal stream): “Where” pathway(movement, contrast 인식)
• 손상: akinetopsia(동작 인식 X)
(2) parvocellualar system(ventral stream): “What” pathway(color, form 인식)
• 손상: achromatopsia(색깔 인식 X), prosopagnosia(얼굴인식 X)
3. 안구 반사
1) 동공반사: 빛의 유입량 조절
Haines Atlas of Neuroanatomy 9th ed. pp.263 | (1) 구성: 직접반응과 공감반응 ① 직접반응: 빛을 비춘 눈의 동공 축소 ② 공감반응: 빛을 비추지 않은 눈의 동공 축소 (2) 경로: retinal ganglion cell → optic nerve → optic chiasm → optic tract → 중간뇌의 pretectal area에서 시냅스 → 중간뇌의 Edinger-Westphal nucleus에서 시냅스 → oculomotor n. (CN Ⅲ) parasympathetic preganglionic fiber → ciliary ganglion에서 synapse → short ciliary nerve → 동공조임근 수축 → 동공 축소 (3) 손상 ① Optic n.(input) 이상: 이상이 있는 쪽에 빛을 비추었을 때 직접반응, 공감반응 X ② Oculomotor n.(output) 이상: 이상이 있는 쪽의 동공 수축(직접반응, 공감반응) 일어나지 않음 |
2) 근접반사: 가까운 물체에 초점을 맞춤
(1) 과정
① Oculomotor n. (CN III) → 양쪽 Medial Rectus 수축 → 양 눈이 가운데로 모임
② EW nucleus → Ciliary Ganglion → ciliary m. 수축 → 렌즈 두꺼워짐
③ EW nucleus → Ciliary Ganglion → sphincter pupillae m. 수축 → 동공 축소
4. 안구의 조직학
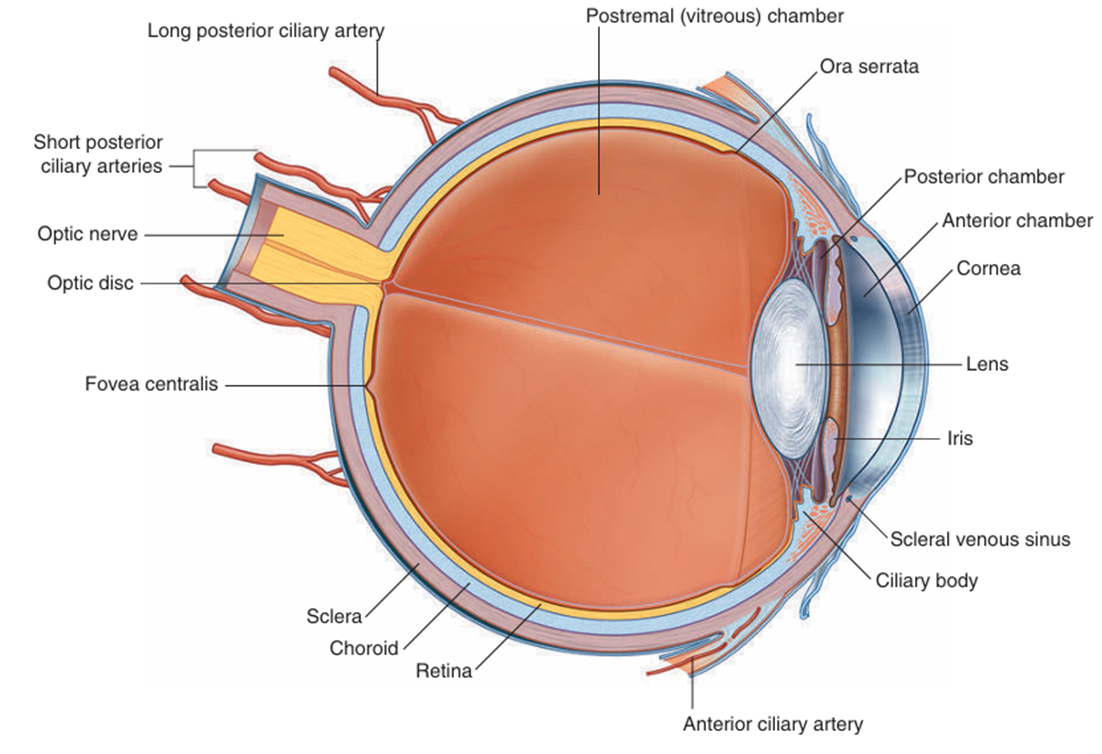
1) 안구의 구조: 바깥섬유층 – 중간혈관층 - 속망막층
Gray’s anatomy for students 4th ed. pp.936 | (1) 바깥섬유층 ① 공막(sclera) ② 각막(cornea) (2) 중간혈관층 ① 맥락막(choroid) ② 섬모체(ciliary body) ③ 홍채(iris) (3) 속망막층(망막, retina) ① 색소층(pigmented layer) ② 신경층(neural layer) |
(1) 바깥섬유층
① 공막(sclera): 6/5 차지, 흰색 층
② 각막(cornea): 눈동자 부분 차지, 투명한 층
• 구성: epithelium(재생가능) - Bowman’s membrane – stroma – Descemet’s membrane – endothelium
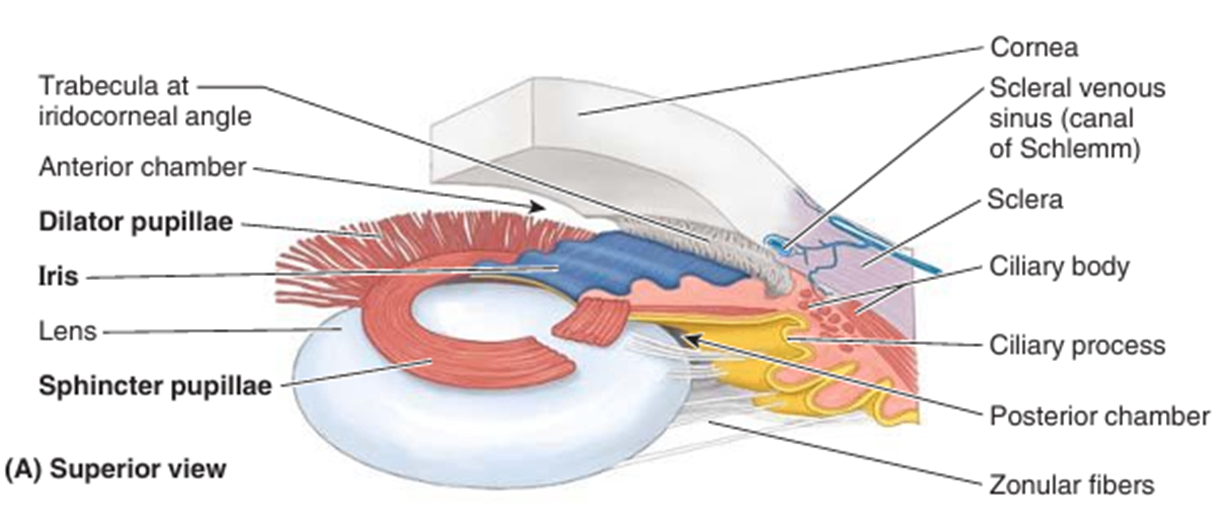
③ Limbus: 각막과 공막의 연결부; 방수가 흡수되는 trabecular meshwork 존재
(2) 중간혈관층
① 맥락막(choroid): 혈관 풍부
• 구성: SCL(suprachoroidal lamina) - CCL(choriocapillary lamina)
② 섬모체(ciliary body)
• ciliary m.: 수정체 두께 조절
• ciliary process: 방수 생산
③ 홍채(iris): 동공의 크기를 조절해 유입되는 빛의 양 조절
• 앞쪽에 상피세포 없음
(3) 속망막층(망막, retina)
① 색소층(pigmented layer): 빛 흡수, 신경층에 영양공급
• 하나의 세포층
• 망막박리: 색소층과 신경층 사이가 벌어진 경우
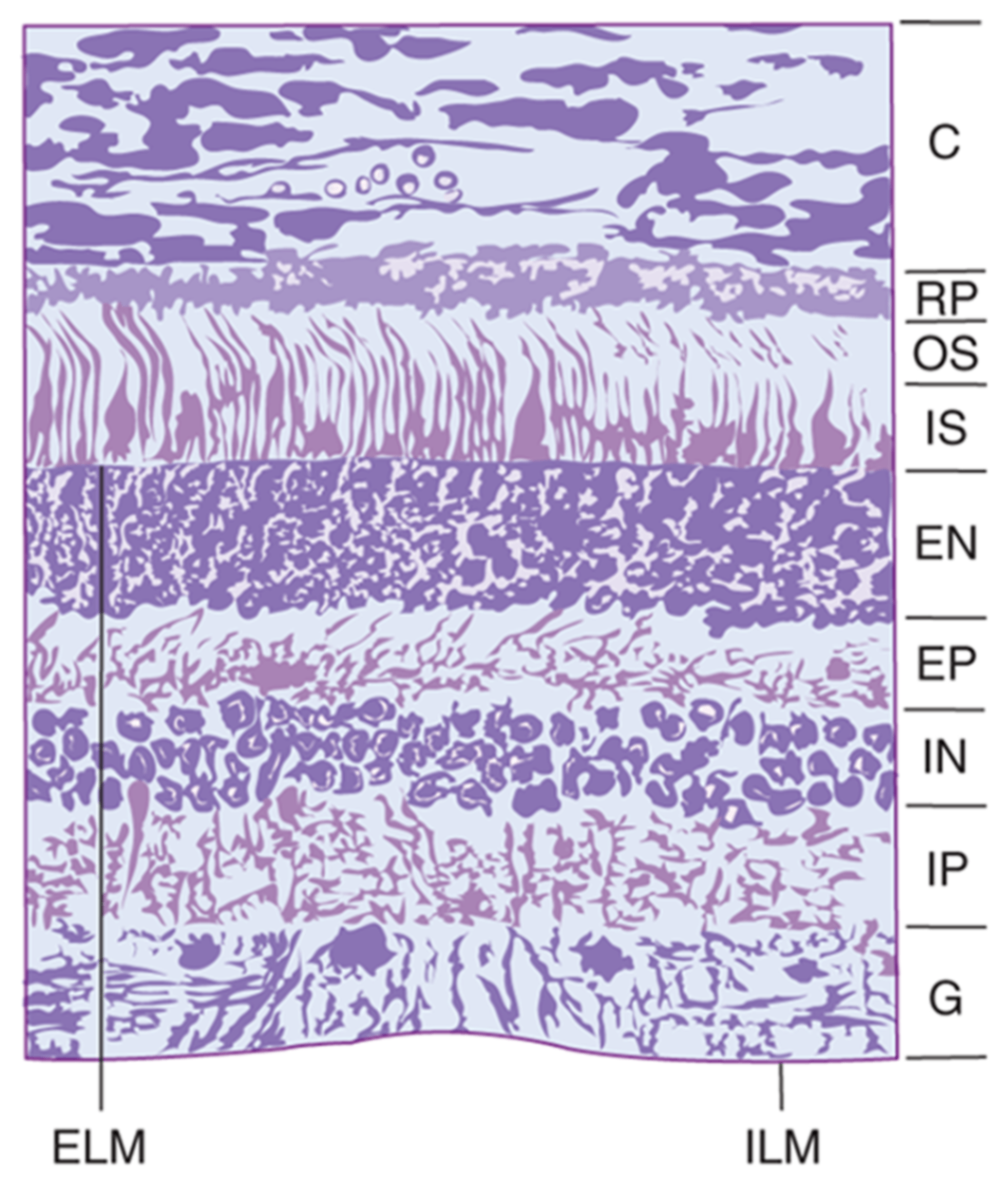
② 신경층(neural layer): 빛 신호를 뇌로 전달
Waxman clinical neuroanatomy 29th ed. pp.198 | C: choroid RP: retinal pigment epithelium OS: outer segments of rods and cones IS: inner segments of rods ELM: external limiting membrane EN: external nulcear layer EP: external plexiform layer IN: internal nuclaer layer IP: internal plexiform layer G: ganglion cell layer ILM: internal limiting membrane |
세포 | 세포체 위치 | 시냅스 상대 | 시냅스 위치 | |
Muller cell | inner nuclear layer | |||
photoreceptor cell | outer nuclear layer | horizontal cell, bipolar cell | Outer plexiform layer | |
interneuron | horizontal cell | inner nuclear layer | Photoreceptor cell | Outer plexiform layer |
bipolar cell | ||||
Retinal Ganglion cell | Inner plexiform layer | |||
amacrine cell | ||||
retinal ganglion cell | ganglion cell layer | dendrite – bipolar cell, amacrine cell axon – optic n. 형성 | Inner plexiform layer | |
• 중심오목(fovea centralis): 정면의 상이 맺히는 해상도가 가장 높은 부위
• 황반(macula lutea): 중심오목 주변의 누렇게 보이는 부위
• 시신경반(Optic disc): 망막의 시신경들이 모여 나가는 부위, 맹점에 해당
2) 앞방과 뒤방: 홍채 기준 구분
(1) 앞방(anterior cavity): 홍채 앞
• aqueous humor(방수)로 채워짐
(2) 뒤방(posterior cavity): 홍채 뒤
• vitreous humor(유리체)로 채워짐
4) 방수
(1) 생성: 섬모체돌기(ciliary process)
(2) 순환: 섬모체돌기(ciliary process) → 뒤방 → 동공 → 앞방
→ 홍채각막구석의 trabecular meshwork → 공막정맥굴(scleral venous sinus, canal of Schlemm)
(3) 흡수: 공막정맥굴(scleral venous sinus, canal of Schlemm)
5. 눈물샘
1) 눈물의 기능: 안구 보호, 굴절을 통한 시야 확대
2) 눈물층의 구조 및 생산
(1) mucin layer: 결막의 goblet cell
(2) aqueous layer: 눈물샘
(3) lipid layer: 눈꺼풀의 마이봄샘, Zeiss 샘
Reference
• Grays Anatomy for Students 4th ed. pp.916-941
• Moore Clinically Oriented Anatomy 8th ed. pp.897-921
• Haines Atlas of Neuroanatomy 9th ed. pp.262-275
• Waxman clinical neuroanatomy 29th ed. pp.197-210
두경부
얼굴
두경부
귀
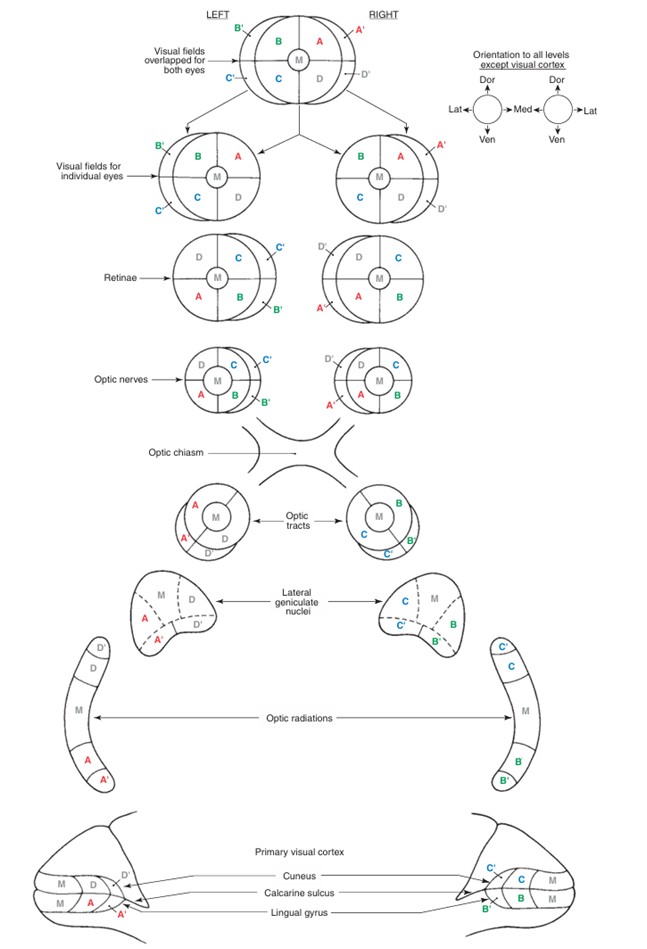 Haines Atlas of Neuroanatomy 9th ed. pp.265
Haines Atlas of Neuroanatomy 9th ed. pp.265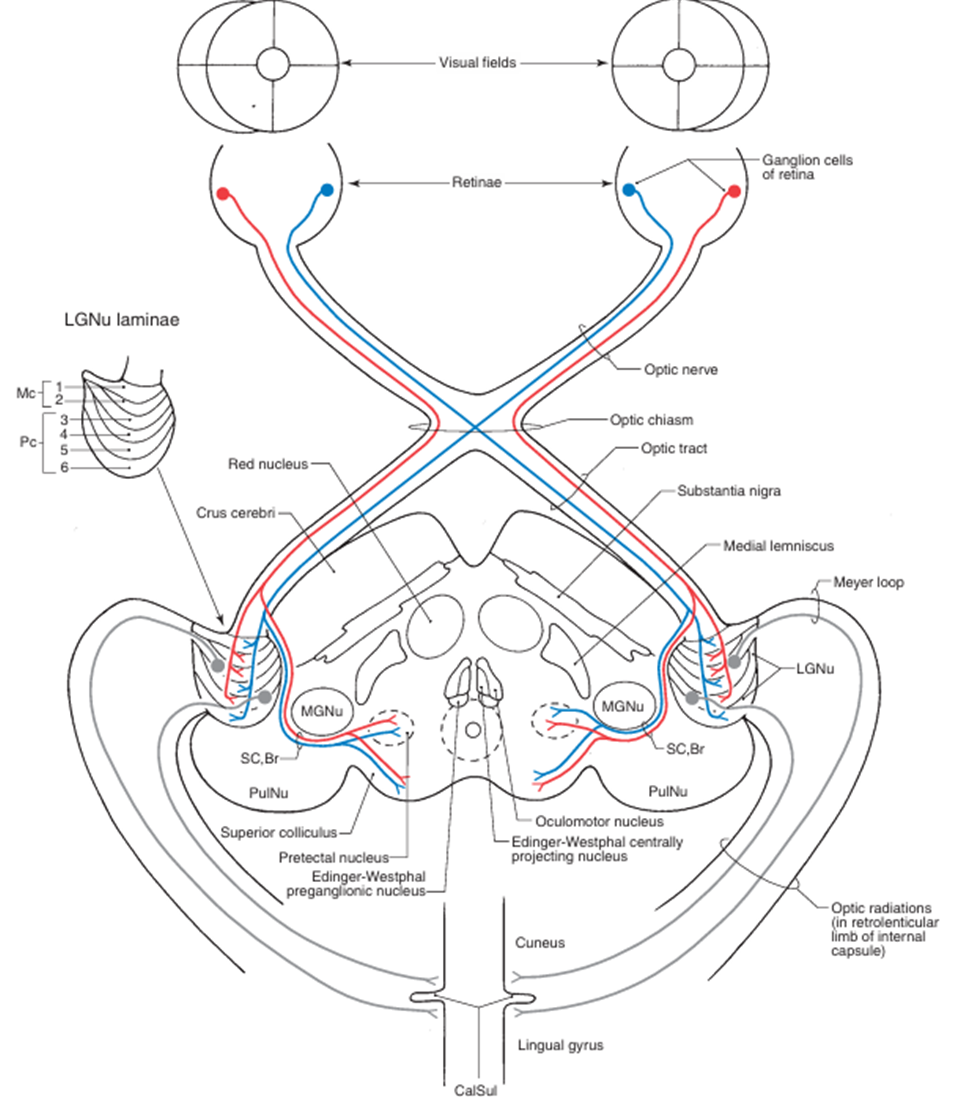
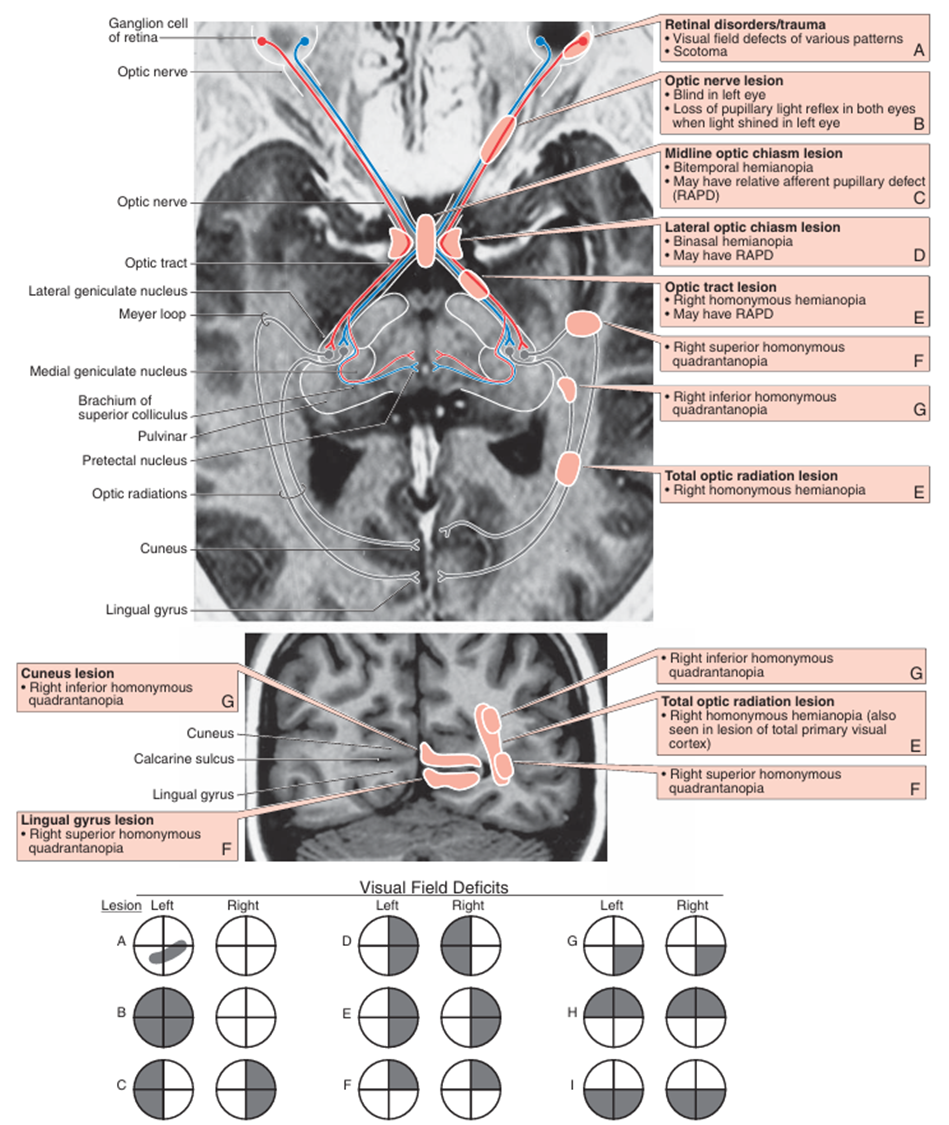 Haines Atlas of Neuroanatomy 9th ed. pp.267
Haines Atlas of Neuroanatomy 9th ed. pp.267