뇌하수체의 조직학
뇌하수체의 조직학
1. 뇌하수체의 구조
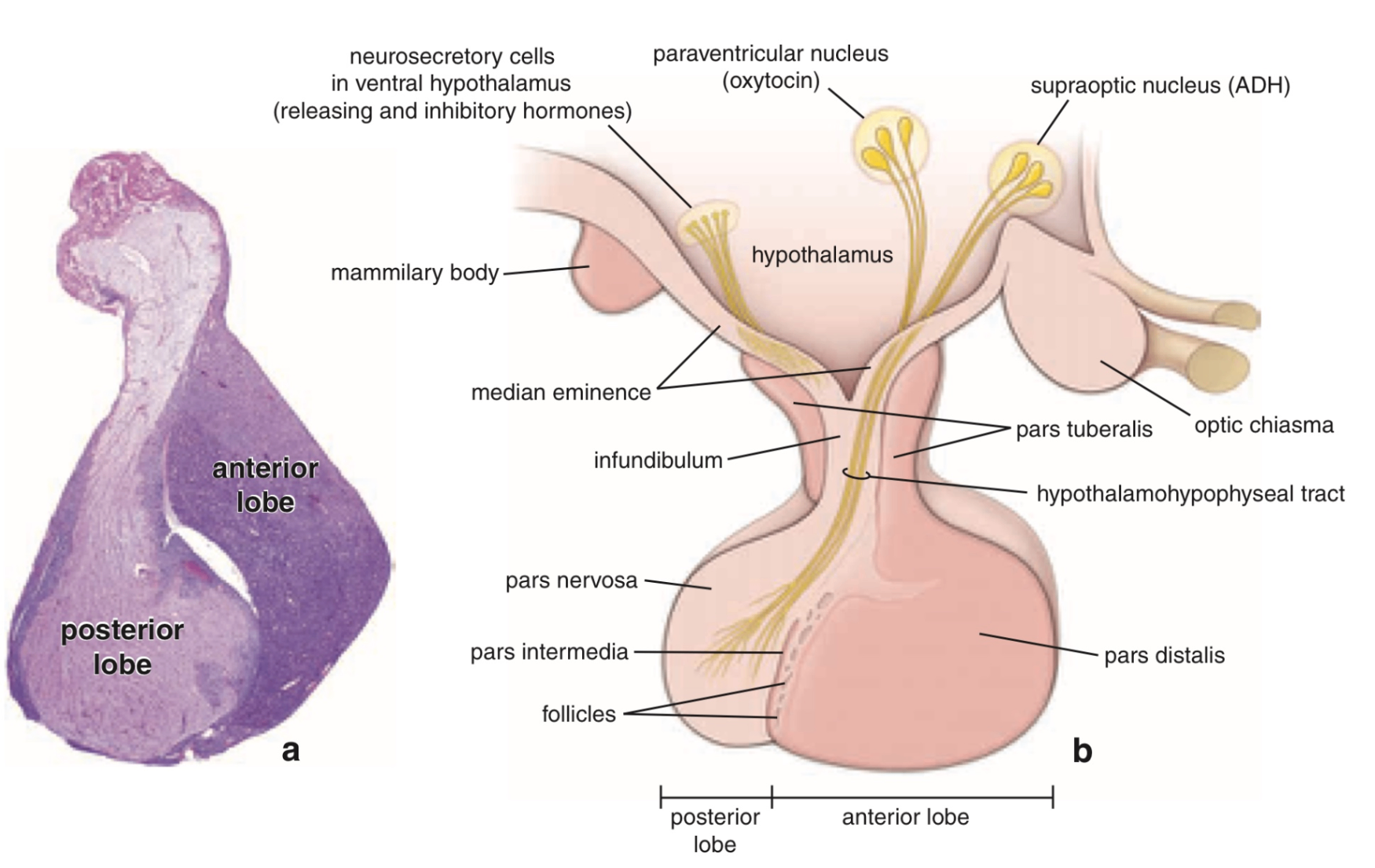
• 두 개의 주요 엽으로 나뉨:
① 전엽 (Anterior lobe) = 선뇌하수체 (Adenohypophysis)
② 후엽 (Posterior lobe) = 신경뇌하수체 (Neurohypophysis)
• 뇌하수체는 시상하부(hypothalamus)와 밀접하게 연결되어 신경 및 혈관 경로를 통해 호르몬 조절을 받음.
1) 전엽 (anterior lobe)
• Pars distalis: 전엽의 대부분 차지, 주요 내분비 세포 존재
• Pars intermedia
• Pars tuberalis: infundibulum을 감싸는 얇은 층; 혈관 풍부
2) 후엽 (posterior lobe)
• 후엽은 자체적으로 호르몬을 합성하지 않고, 시상하부에서 만들어진 것을 저장/분비만 함
• Pars nervosa: 후엽의 대부분 차지, 시상하부의 시신경세포 축삭 말단이 위치
• Infundibulum: 뇌하수체 줄기, 시상하부와 후엽을 연결하는 축삭 통로
• Hypothalamo-hypophysal tract: 시상하부의 신경핵에서 후엽까지 이어지는 축삭; 호르몬의 수송 경로
2. 뇌하수체 분비 호르몬
1) 전엽
호르몬 | 기원 세포 | 표적기관 | 주요 기능 |
|---|---|---|---|
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) | Corticotroph | 부신겉질 (adrenal cortex) | Glucocorticoid (Cortisol) 분비 촉진 |
TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) | Thyrotroph | 갑상선 (thyroid) | T3/T4 (갑상선호르몬) 분비 촉진 |
GH (Growth hormone) | Somatotroph | 간, 전신 조직 | IGF-1 유도, 성장 촉진, 단백질 합성 ↑ |
PRL (Prolactin) | Lactotroph | 유선 (mammary gland) | 유즙 생성 촉진 |
FSH (Follicle-stimulating hormone) | Gonadotroph | 생식샘 (난소/고환) | 난포 성숙, 에스트로겐 생성 / 정자 생성 촉진 |
LH (Luteinizing hormone) | Gonadotroph | 생식샘 (난소/고환) | 배란, 황체형성 / 테스토스테론 분비 촉진 |
MSH (Melanocyte-stimulating hormone) | Pars intermedia | 멜라닌세포 | 멜라닌 합성 (사람에서 역할은 미미) |
2) 후엽
호르몬 | 생성 장소 | 표적기관 | 주요 기능 |
|---|---|---|---|
ADH (Antidiuretic hormone, Vasopressin) | 시상하부 supraoptic nucleus → 후엽에서 저장·분비 | 신장 집합관 | 수분 재흡수 ↑ → 요농축, 혈압 상승 |
Oxytocin | 시상하부 paraventricular nucleus → 후엽에서 저장·분비 | 자궁, 유선 | 자궁 수축 (분만), 유즙 분비 유도 (사출) |
Reference: Histology: A Text and Atlas, Wolters Kluwer, 7th edition
조직학
근육의 조직학
조직학
위샘의 조직학